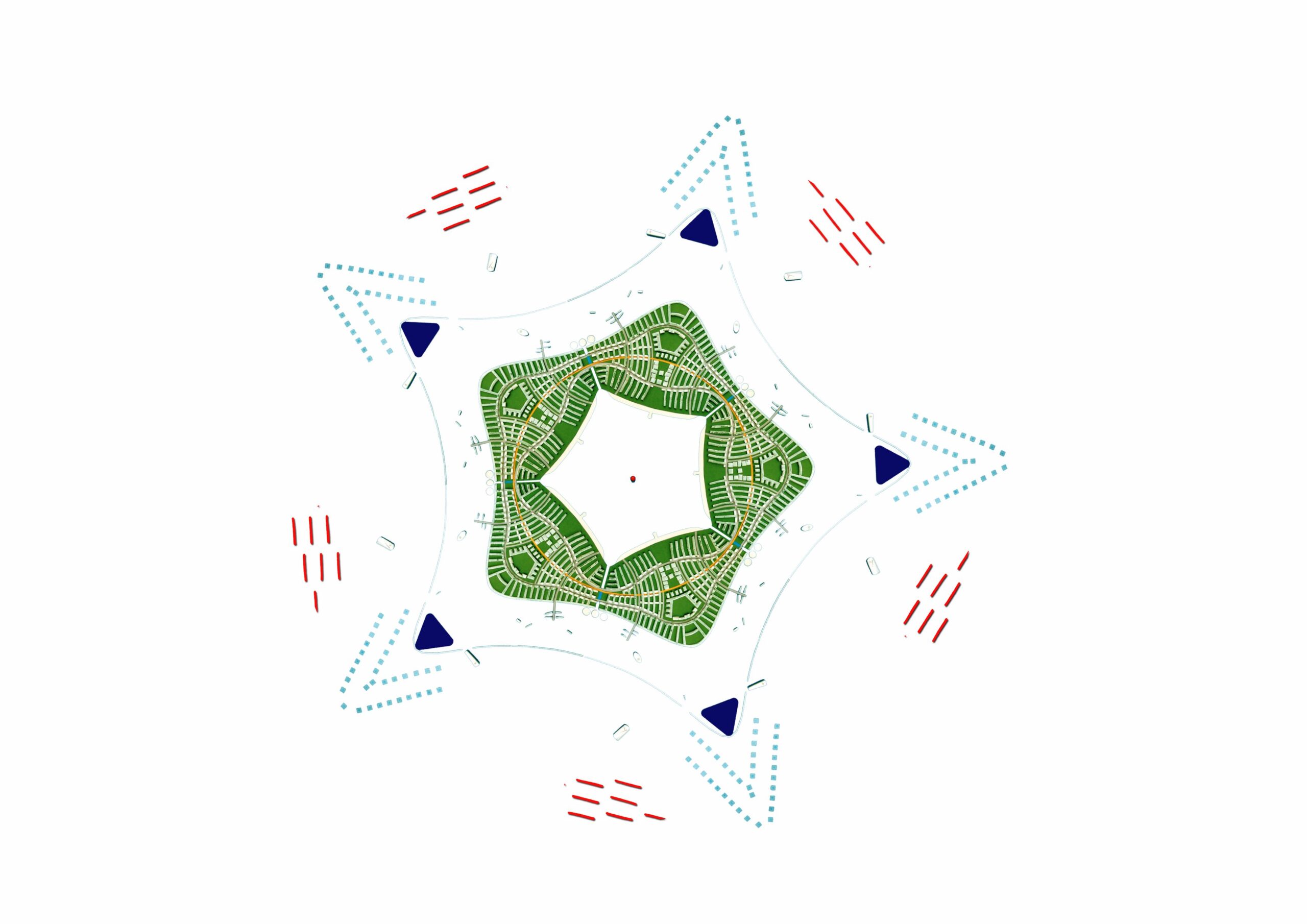
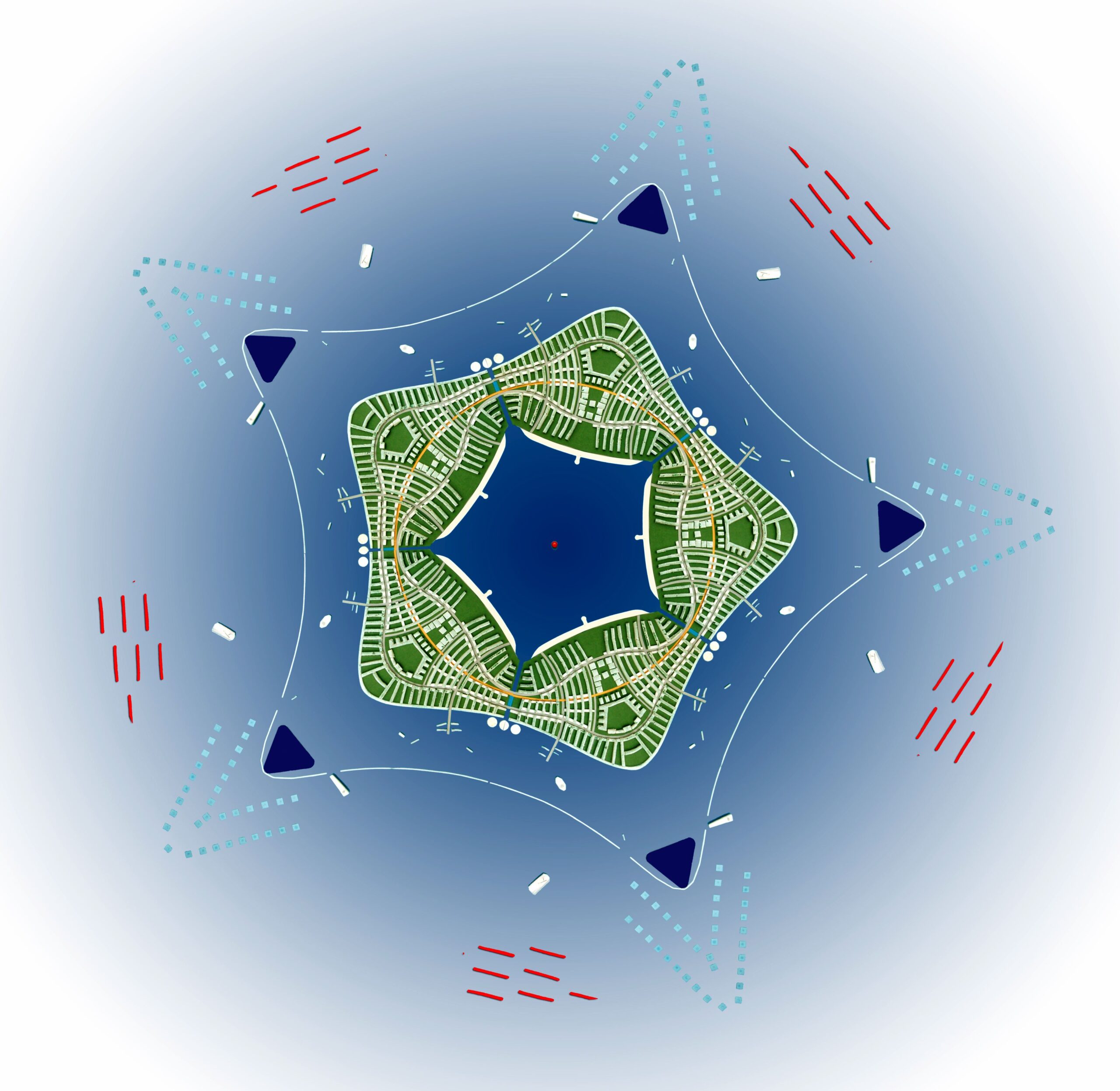
Sea Star City is a way of dealing with the major problems that confront humanity and human settlements. Sea Star will be a self-sufficient, very densely populated settlement with a huge hinterland (hinter-water actually). The sea places natural limits on the growth of the city. The pattern of development that many planners have proposed but never succeeded in creating on land happens easily on the water. Urban sprawl is automatically taken care of and the area for gathering natural resources is available in plenty.
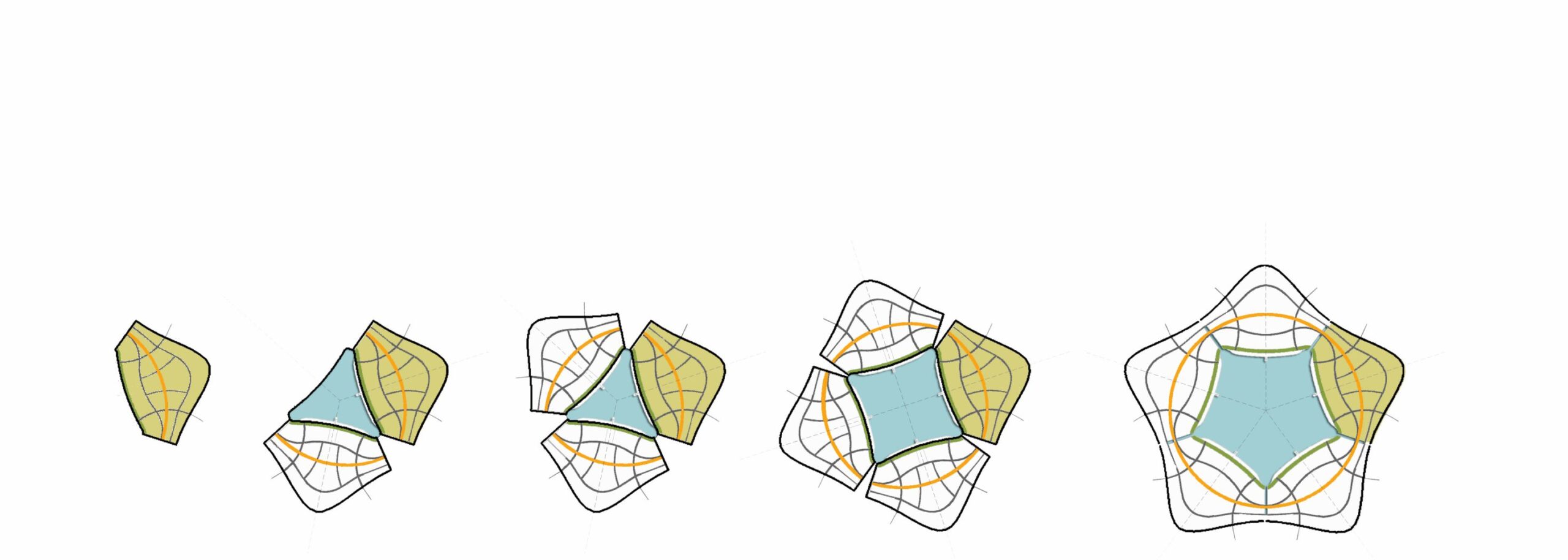
Sea Star City will deal with the problems of global warming, and scarcity of food, water, energy and land. It will be a growing city compactly planned and made of lightweight composite materials. The first sector of Sea Star City will be built with United Nations Fund for refugees from island states that rising seas will submerge. It will be located close to the continental land mass. The other sectors of Sea Star will be built by residents who move to the first sector. More Sea Stars will be built as seas rise further and submerge other islands.
Sea Star is not just a city for climate change refugees. It is the way of making sustainable settlements that help prevent climate change.
What is a self-sufficient city?
Cities are places where human beings live and produce industrial goods or provide services. They can become self-sufficient only if they can produce their own food, energy and water. They must also be able to take care of their waste. Above all, a self-sufficient city must have a strong economic basis.
Cities in emerging economies and developing countries
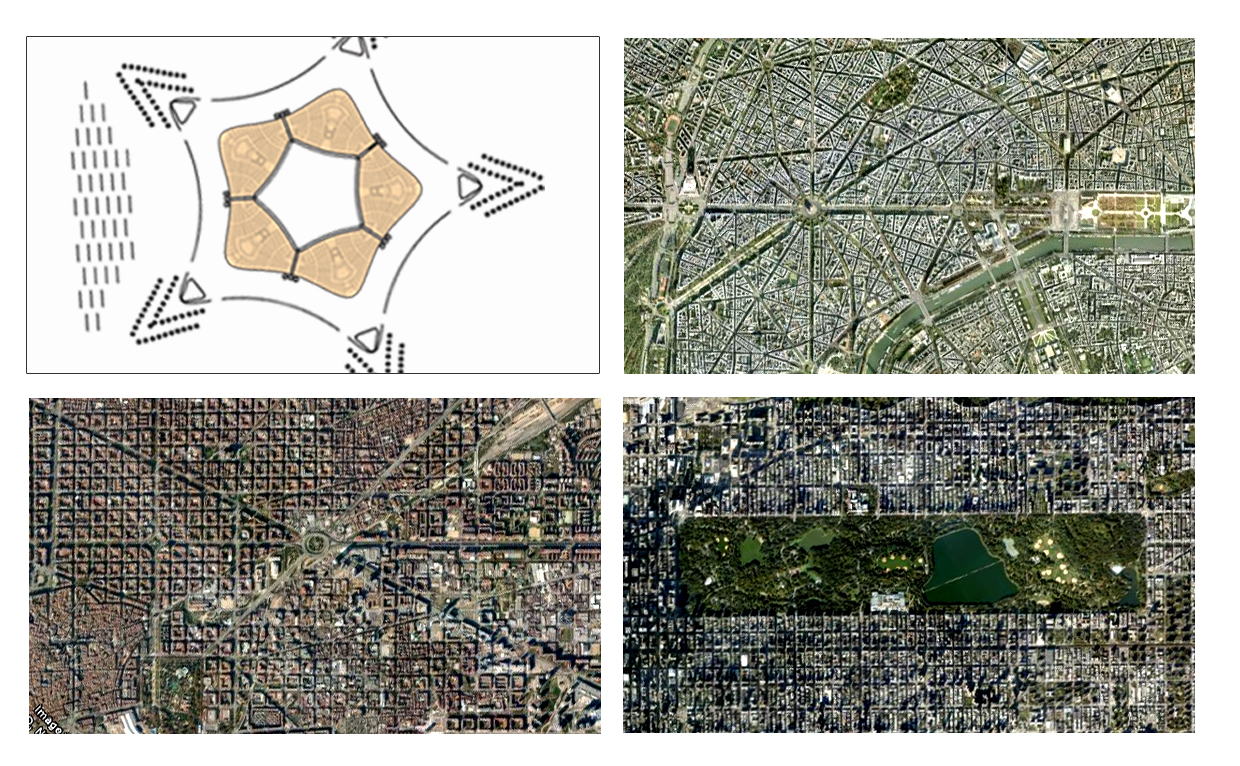
New sub-cities are constantly being added to existing cities in emerging economies like India and China. Such accretions are never self-sufficient. In India, new cities have to compete for land with agriculture, industry and renewable energy. Land for new cities is difficult to come by.
Climate Change
When the mean sea level rises, the existing land mass will shrink and many existing cities with low elevations will disappear. Seas and oceans will swell and enlarge. Climate change will cause problems in water supply and food production. To survive, a new city must have a sustainable source of water and food.
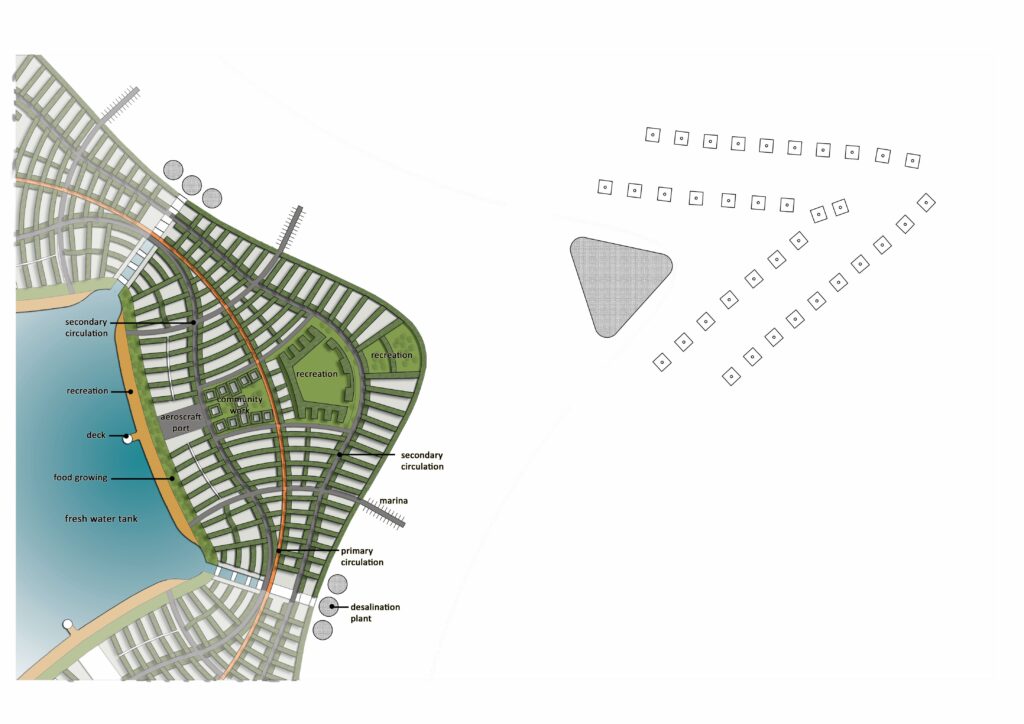
Food
Agriculture alone will not be able to supply food for the future populations of the world. Seafood catches are reducing due to overfishing. Mariculture or open sea aquaculture – the cultivation of seafood like fin fish, shellfish and algae – can enhance the food supply for future populations.
Water
The world’s sources of fresh water are reducing. Rain over the sea and desalination of seawater using solar energy will provide fresh water in abundance.
Energy
Harnessing renewable energy requires area. Wind energy has limited sites and solar energy requires land. The oceans have wave energy additionally and no limitations of area for solar energy. Wave and solar are complementary sources of energy.
Transport
Personal motorised transport in cities uses up a great deal of energy and causes pollution. Public transport does not work well in spread-out cities. Dense, compact cities are able to function well with walking, cycling and public transport and without cars.
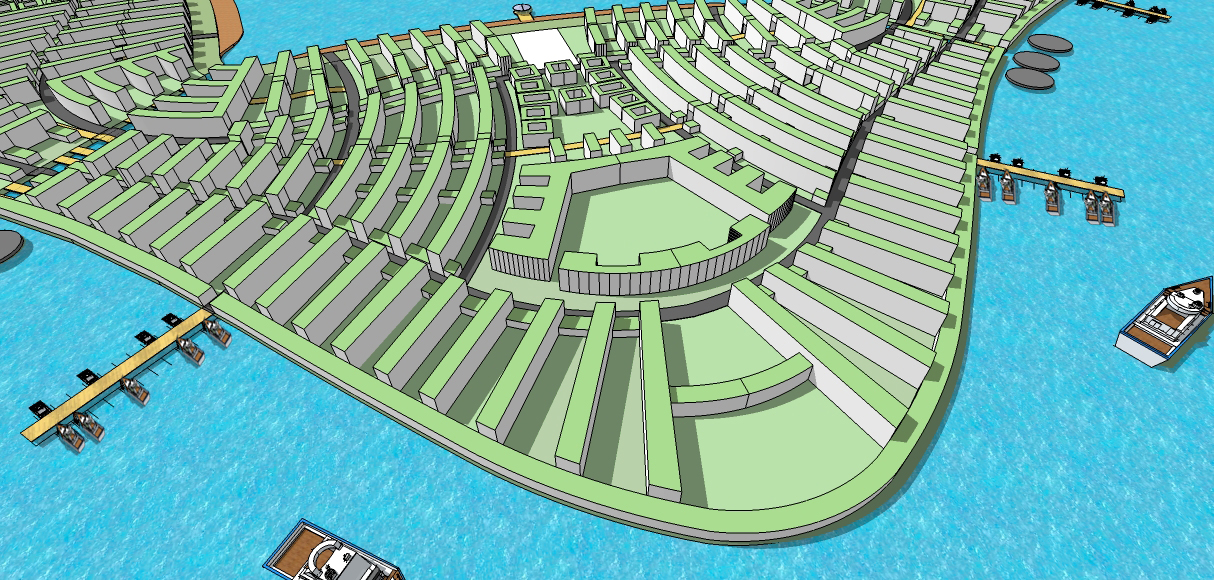
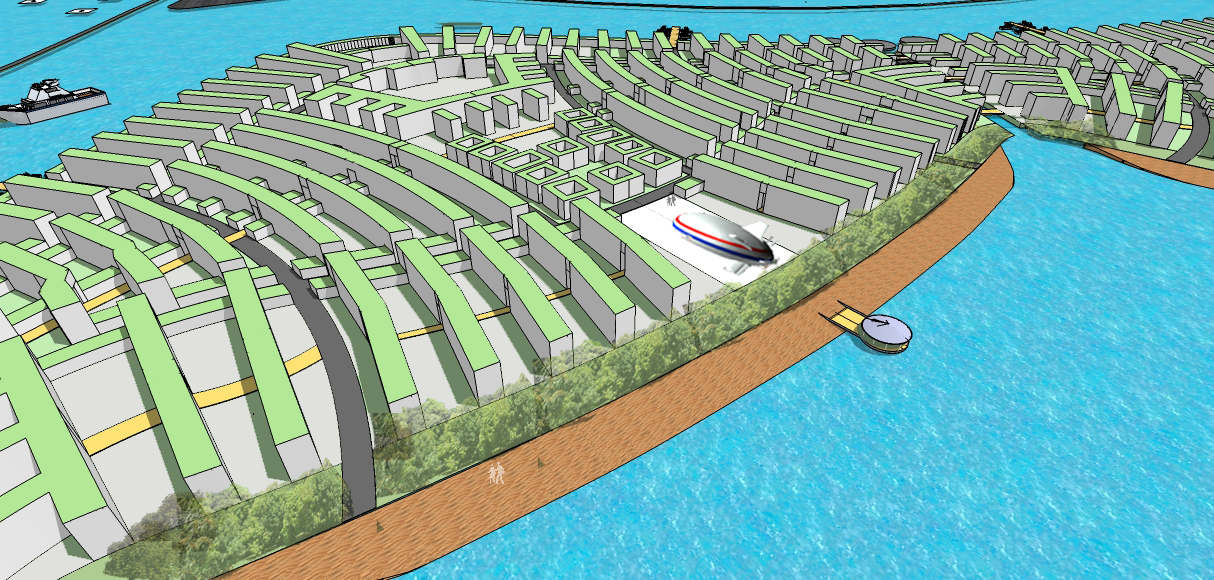
Building on water
Water is the logical place for building new cities. Cities built on reclaimed land are subject to inundation when the sea level rises. A floating city will be able to deal with the problem of long-term and short-term changes in sea level. Aquaculture will provide food, work and the economic basis for the floating city. There will be an abundance of water and renewable energy in a city on water.
Materials
Cities on the sea will have to deal with the problems of import of construction materials at a high cost. It may be possible to grow materials from seawater or extract them from the ocean bed. Sea-Crete is one such material for which technology is available.
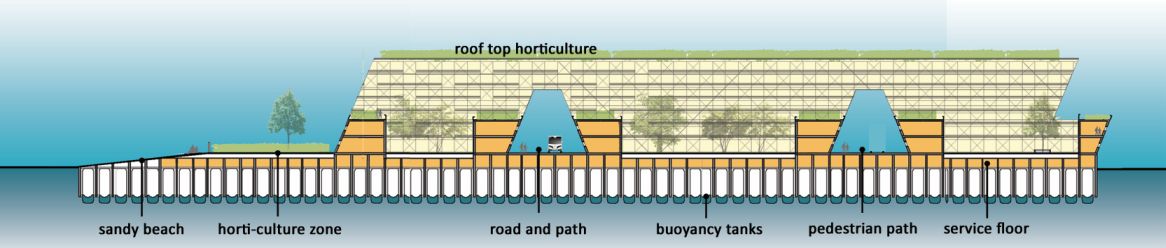
Facts:
Total platform area: 165 Ha
Area of one sector: 33 Ha
Area for rainwater harvesting: 57 Ha
Total Population: 180,000 persons
Built-up space: 3.28 million sqm
Area for horticulture: 90 Ha
Area for open sea aquaculture: unlimited
Area for wave energy converter: unlimited
Area for solar photo-voltaic: unlimited
Area for solar desalination: unlimited



