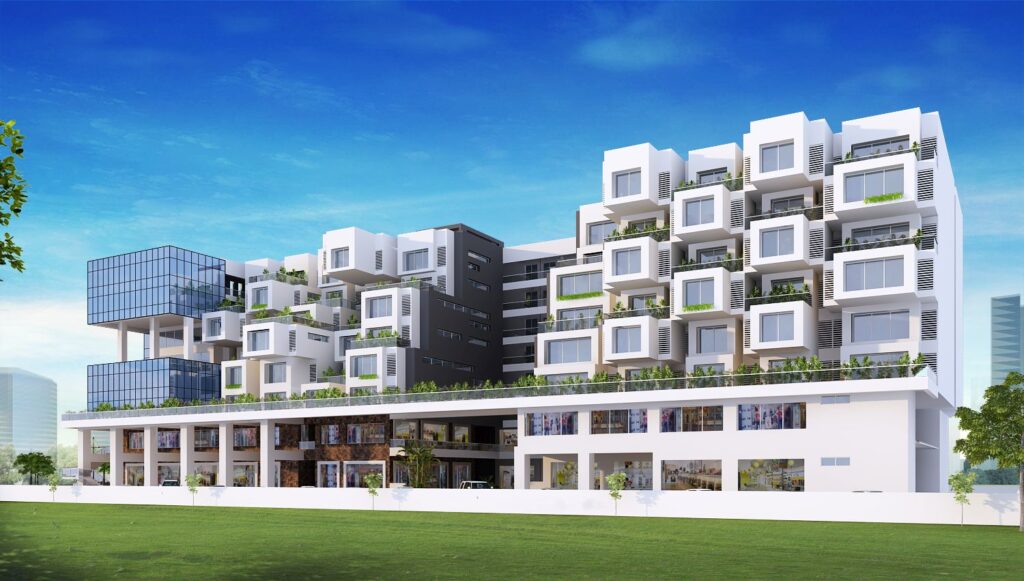
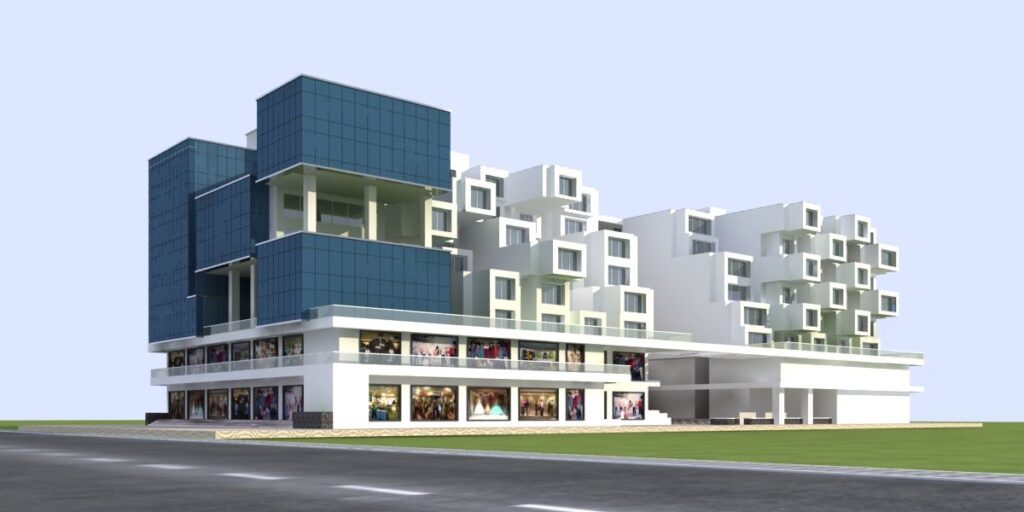
The terraces is a commercial building in scheme no. 54, Indore.
The building is an environmental filter, an analogy for synthesis & analysis. The vision behind this project is to uncover ‘the relationship of buildings, landscape & climate’ transforming the impact of commercial development in the ecosystem of a city.

Function and use
This is a commercial project equipped with shops on ground & 1st floor & offices on the above floors
Physical parameters
A mixed use development.
Basement and lower basement completely dedicated to parking.
Ground and first floor having 44 shops.
Second till seven floor having 132 offices.

Site Justification
Site is rectangular in shape having longer facades on west & east & shorter facades on north & south. The approach road to the site is from south direction.
Climate of Indore
Indore has a humid subtropical climate and savanna climate. Indore gets moderates rainfall during July- September due to the southwest monsoon.
Soil Type
Black cotton soil have typical characteristics of shrinkage and swelling due to moisture. In addition to this, these soils have very poor bearing capacity.
Observation and Inspiration
- Only leisure space in an office building may be cafeteria or the office pantry; thus this was one of the impactful observation.
- Architectural principles no longer apply when a building acquires “bigness”. Current trend in Indore’s office buildings has set the biggest inspiration as nowadays in Indore exists bigness & hugeness, concrete giants with glass facades.
This monotous trend has forced the design to incorporate something new & innovative in this direction- giving importance to terms like energy saving, comfort level, etc.
- To give a contemporary look or contemporary architecture not only means huge giant concrete exoskeleton with glass facades or curtain walling.
- A building can also live more & more years & this is possible only on the basis of planning, circulation & natural light-ventilation.
- Issues like energy-saving, climate consciousness & occupancy comfort was not realized yet.
- Visual connectivity is missing.
Evolution of form
These are all office buildings in Indore. Gigantic box type architecture & achieving maximum FSI.
These massy cubes are made up of concrete, glass & aluminum panels.
This type of architecture set the biggest inspiration to think something new & innovative in this direction.
A roof garden can be distinguished from a green roof, the term roof garden is well suited to roof spaces that incorporate recreation, entertaining, and provide additional outdoor living space for the building’s residents. It may include planters, plants, dining and lounging furniture, outdoor structures such as pergolas and sheds, and automated irrigation and lighting systems.
The observations & inspirations has helped to evolve & generate the ideas & concept accordingly in this context.
Design demanded to overcome the typical heat-island effect by creating positive design responses to wind & shade as well as introducing vertical landscape, the use of heat-sink cladding & reduction of air-conditioning use.
Additionally, architect incorporates transitional spaces from exteriors to interiors, the principles of identity & regionalism & extensions of the land & garden.
Natural ventilation is the process of supplying air to and removing air from an indoor space without using mechanical systems. It refers to the flow of external air to an indoor space as a result of pressure differences arising from natural forces.



Principles of design include
Responding in plan & form to the climate.
- Responding to the landscaping by introducing planting upwards & diagonally across the face of the built forms.
- Breaking surfaces from the straight planes to planes in the context of the site.
- Linkages to the ground & surrounding base.
- Responding to the modern movement.

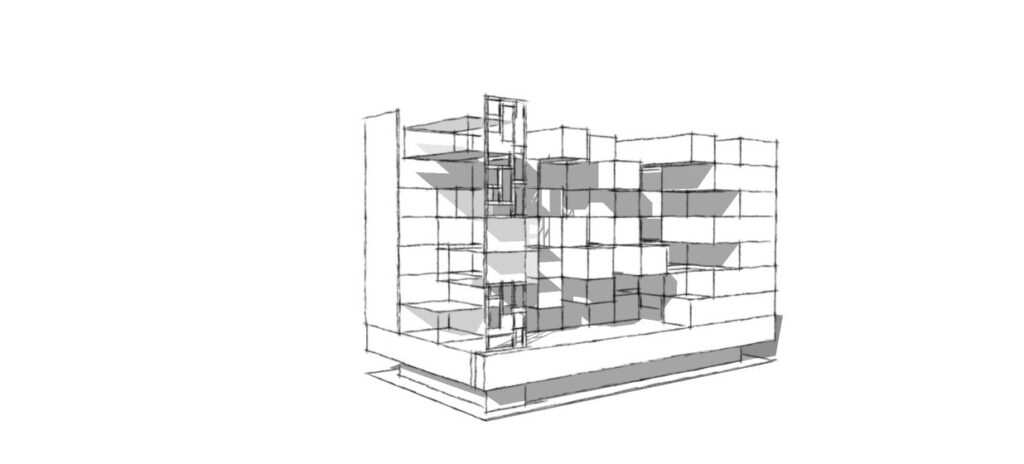
Basic idea
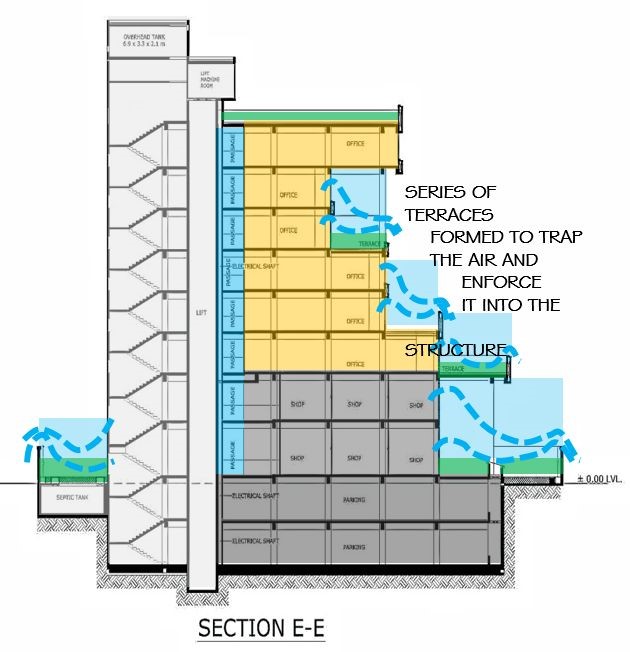
Basic idea generating section on east side green pockets are created & these pockets will receive morning pleasant daylight.
On west side terraces along with double height volumes are generated & so that the wind can flow easily inside the interiors & these terraces will appreciate the sunset.
–the building’s general form, glazed surfaces, green pockets, terraces, double height volumes, etc. Are oriented for maximum environmental efficiency shading against direct overheating but allowing natural daylight and wind flow.
Cross ventilation can be problematic during the winter when windows may be closed, particularly in modern buildings which tend to be highly sealed. Trickle ventilation, or crack settings on windows can be provided to ensure
A roof garden is a garden on the roof of a building. Besides the decorative benefit, roof plantings may provide food, temperature control.
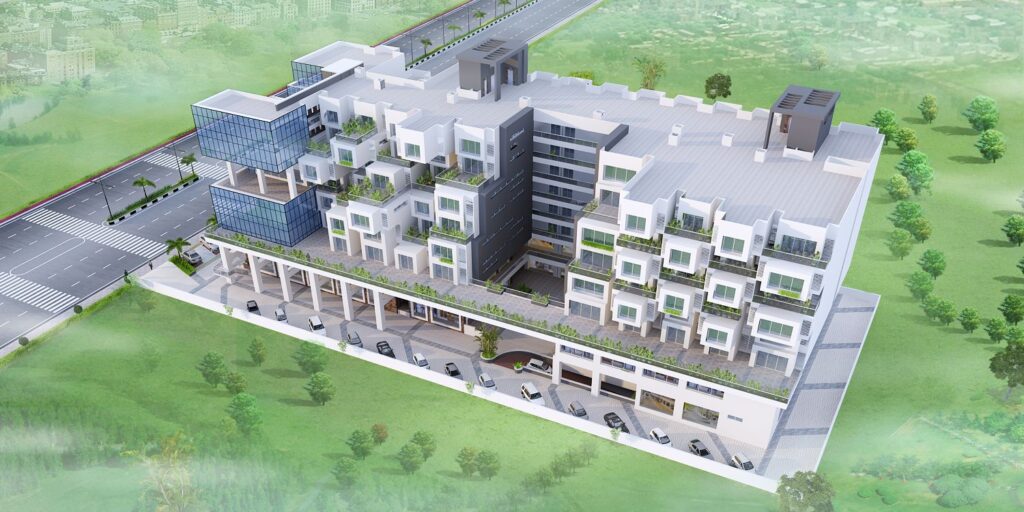

Drawings of The Terraces
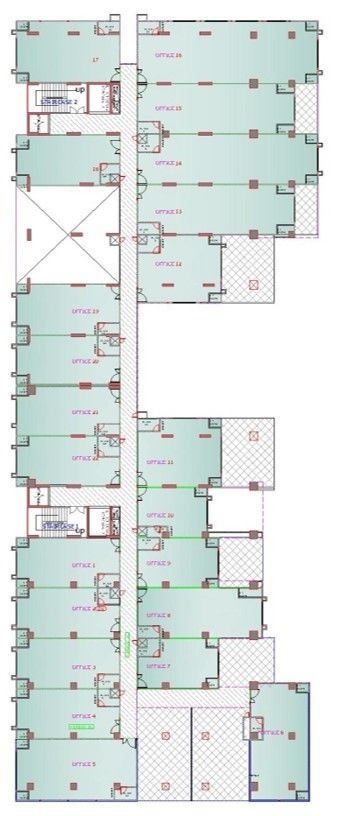

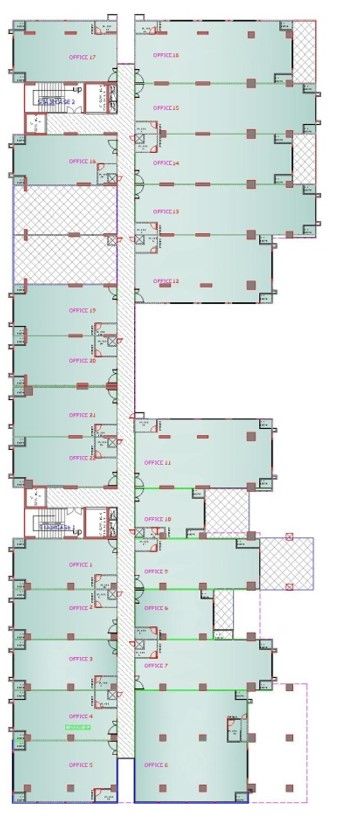
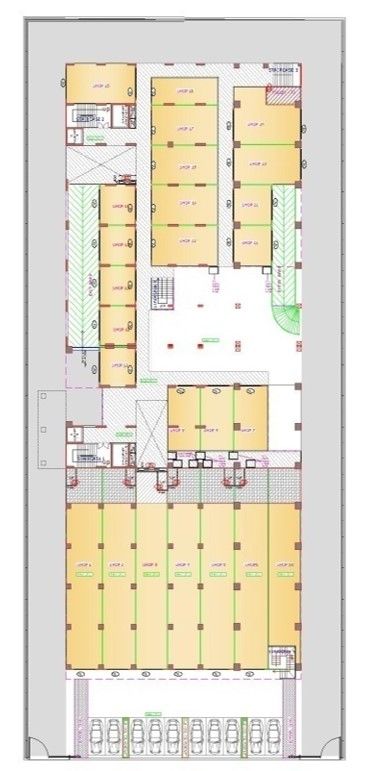
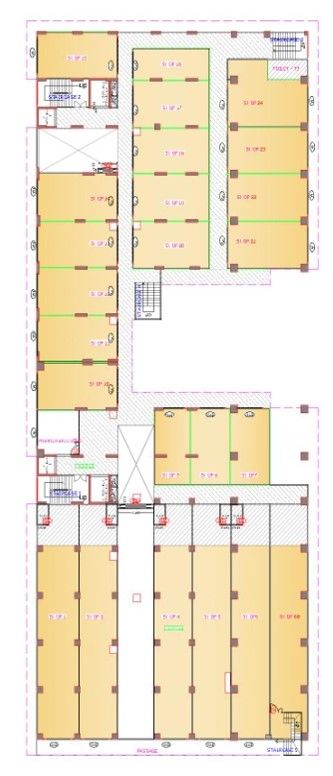
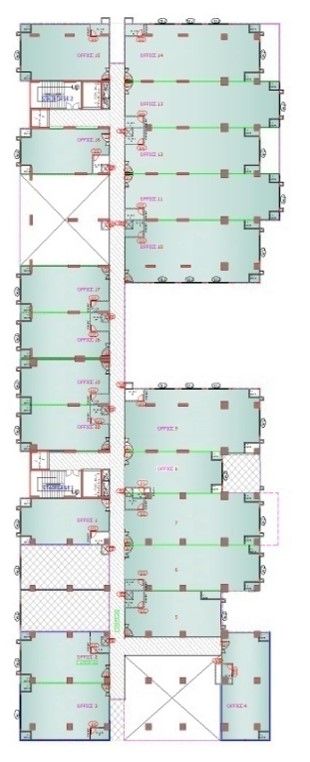
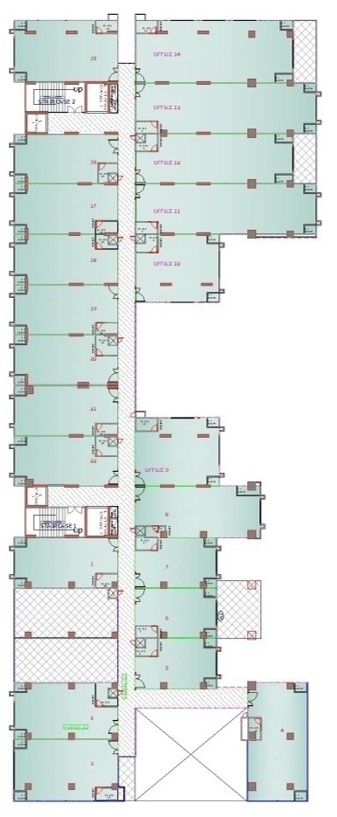
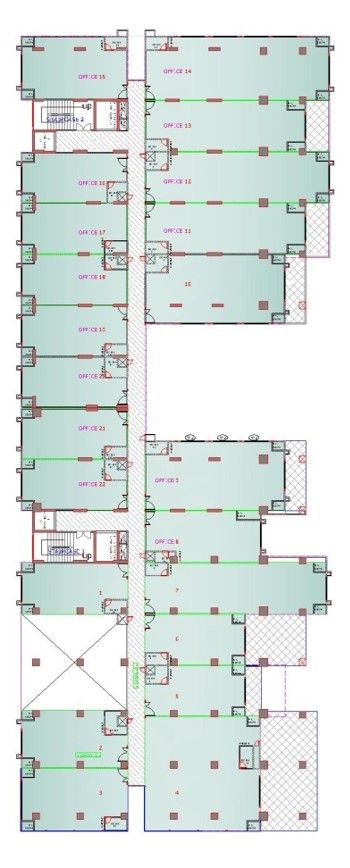
Project Facts
Place of the project- a. B. Road, Indore
Category- commercial
Site area- 4538.40 sq. Mts.
Total built-up- 11336.20 sq. Ft.
Height- 31.70 mts
Floors over ground- 6
Floors underground- 2
Ground coverage- 2437.61 sq. Mts.